A septic system is a self-contained wastewater treatment setup that serves properties not connected to municipal sewer lines. It's a practical and eco-friendly solution for rural homes and those in areas without centralized sewage facilities.
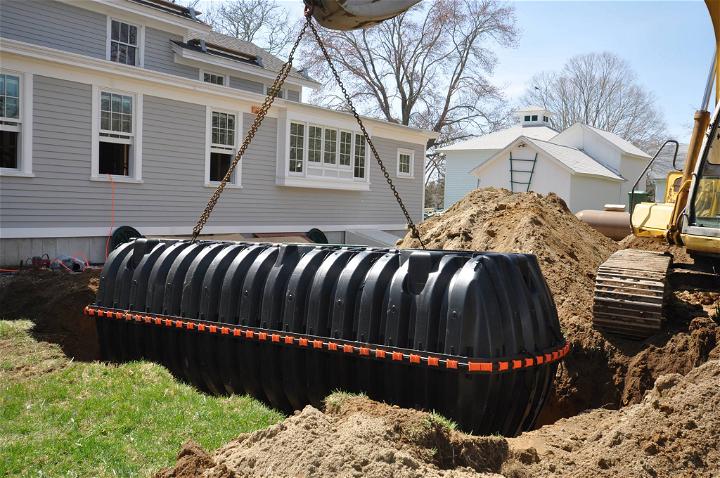

How Does a Septic System Work?
The system typically consists of a septic tank and a drainfield. Wastewater from your home flows into the septic tank, where solids settle at the bottom, and lighter materials like fats and oils rise to the top. The middle layer of partially clear water, known as effluent, then moves to the drainfield. Here, it percolates through the soil, which acts as a natural filter, removing harmful bacteria and nutrients.
Planning and Design of Septic Systems
Building an effective septic system requires careful planning and design, tailored to your property's unique characteristics.
Assessing Your Property
A professional assessment is crucial to determine the best system type and location, considering factors like soil type, property size, and proximity to water sources.
Understanding Local Regulations
Compliance with local health and environmental regulations is essential. These rules dictate system design, including tank size and drainfield specifications.
Designing for Efficiency and Sustainability
The system should be designed to handle the specific wastewater output of your household while minimizing maintenance and environmental impact.
How to Install Septic Tank - Step by Step Guide
Learn to install your own septic tank with our easy DIY septic tank installation guide, covering step-by-step instructions, maintenance, and more.
Step by Step Instructions
Step 1: Understand Your Requirement
Before diving into the installation, clearly understand your requirements based on the number of bedrooms and bathrooms in your home. This will determine the size of the septic tank you need. For example, a home with five bedrooms will need a tank designed for a 750-gallon per day flow rate, equating to a 1500-gallon tank.
Step 2: Soil Evaluation
The very first professional step involves conducting a soil evaluation or a perk test. This step is necessary for determining the absorption rate of your soil, which directly influences the design of your septic system. Usually, this requires the digging of three holes in your property for testing.
Step 3: Acquiring Permits
Using the data from your soil evaluation, prepare the necessary paperwork for your local permits. This includes the design of your septic system and a detailed site plan. The costs associated with these permits vary by location, but it's a mandatory step before any digging begins.
Step 4: Sizing the Tank and System
Using the number of bedrooms and bathrooms to determine the daily flow rate and the soil absorption rate from your perk test, calculate the size of your septic tank and the design of your leach field.
Step 5: Installation Preparations
Site preparation involves marking out the layout for your septic tank and leach field based on your design plans, ensuring you adhere to local regulations concerning setbacks from property lines, buildings, and environmental features.
Step 6: Digging and Installing the Tank
Dig a hole for your septic tank that accommodates its size, considering the depth needed for gravity to effectively move wastewater from your house to the tank. Ensure the tank is level when placed into the ground.
Step 7: Connecting to the Leach Field
Dig trenches for your leach field lines, making sure they are spaced properly and at the correct depth according to your design. If using a chamber system, ensure each chamber is correctly connected and leveled in the trench.
Step 8: Installing the Distribution Box
Place and level the distribution box (D-box), ensuring it's set on undisturbed soil to prevent shifting. This box evenly distributes effluent into the leach field lines.
Step 9: Final Inspection
Before you can bury everything and call it done, you need a final inspection from a local official. They will check the level of your tank, the installation of your D-box, and the layout of your leach field to ensure everything meets the required standards.
Step 10: Covering and Wrapping Up
Once you've passed inspection, cover your septic tank and leach field. Remember to maintain access to your tank's inspection ports, perhaps by installing risers for easier location and access.
Maintenance
Maintain your system by cleaning the effluent filter annually and scheduling tank pumping every 3-5 years. Proper maintenance avoids costly repairs and ensures the longevity and effectiveness of your septic system.
Video Tutorial
For a detailed, step-by-step video tutorial on installing your own septic system, watch this excellent guide on YouTube.
It pairs well with this written guide, offering an additional resource that visually explains the process in an easy-to-follow format.
By following steps & ensuring septic system installation meets local regulations, achieve efficient wastewater management at home.
Permitting Process for Septic Systems
Obtaining the right permits is a critical step in the installation of a septic system. It ensures that your system meets local health and environmental standards.
Understanding the Permitting Authority
Your local health or environmental department is typically responsible for septic system permits. They inspect and approve the design and installation of your system to ensure it's safe and effective.
Steps to Acquire a Permit
- Site Evaluation: A professional evaluates your property to determine the suitable type and size of the septic system.
- Application Submission: You or your contractor must submit a detailed application to the local permitting authority.
- Documentation: Provide a copy of your property's septic record drawing and any additional information such as soil properties.
- Approval: Once your application is reviewed and meets all requirements, you will receive the permit to begin installation.
FAQs for Septic Tank Installation
Addressing common questions can help clarify the installation process for homeowners.
Common Concerns
- How do I know if I need a septic system? Check your property records or utility bills; a $0.00 charge for wastewater services usually indicates a septic system.
- Where should the septic tank be placed? It should be on level ground, at a minimum distance from your foundation as required by local regulations.
Installation Queries
- What size tank do I need? The size depends on your household's water usage and the number of residents.
- What materials are used for septic tanks? Common materials include concrete, fiberglass, and plastic, each with different durability and maintenance needs.
By following these guidelines and addressing these FAQs, you can ensure a smoother septic system installation process. Remember to consult with professionals and adhere to local regulations throughout the project.
20 DIY Septic Tank System Plans and Inspirations
Discover 20 DIY septic tank system plans and inspirations to maintain your system efficiently. Save money and prevent costly repairs with these helpful guides.

1. Cheap DIY Tote Septic System
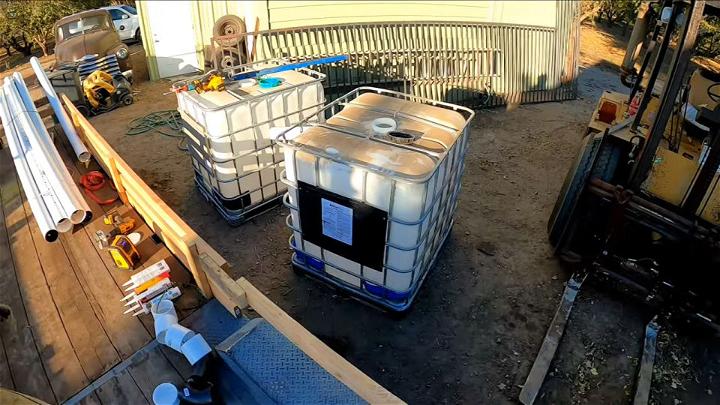

Embarking on building a tote septic system can be a cost-effective and eco-friendly project. Its design makes use of repurposed totes, reducing waste and cutting costs significantly. It's a smart choice for those looking to manage waste sustainably on a budget.
2. Septic System for Your Retreat Property
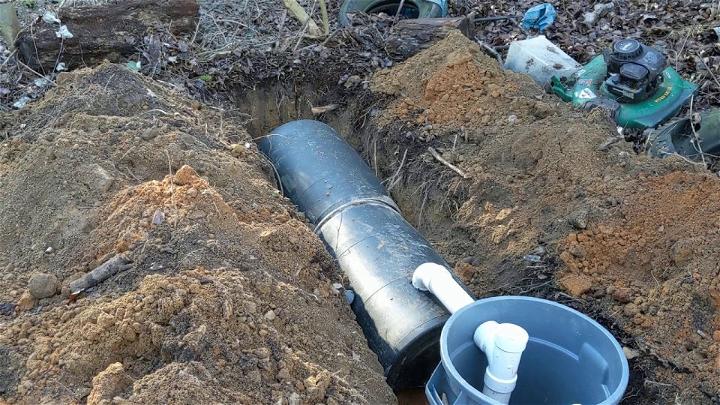

Having a reliable septic system on your getaway retreat is essential. Opting for a system designed for lower usage can reap benefits, ensuring longevity and efficiency. It's an inviting solution for property owners seeking peace of mind in their tranquil escape.
3. Homemade RV Mini Septic System
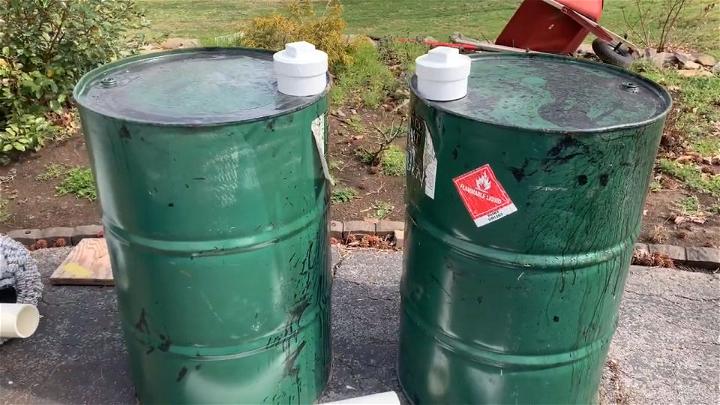

Crafting a mini septic system for your RV adds convenience and sustainability to your travels. This compact setup is tailored for the nomadic lifestyle, offering a portable and environmentally friendly waste management solution that keeps nature pristine and your travels worry-free.
4. Easy Septic Tank Design
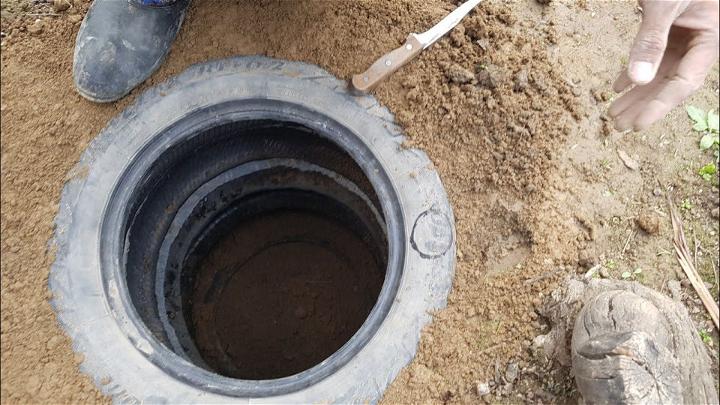

Designing a septic tank doesn't have to be complex. Opting for an easy design that emphasizes straightforward construction and maintenance can simplify the process. It's a welcoming approach for those seeking to implement an effective waste management solution without the complications.
5. Off-Grid Septic System Install
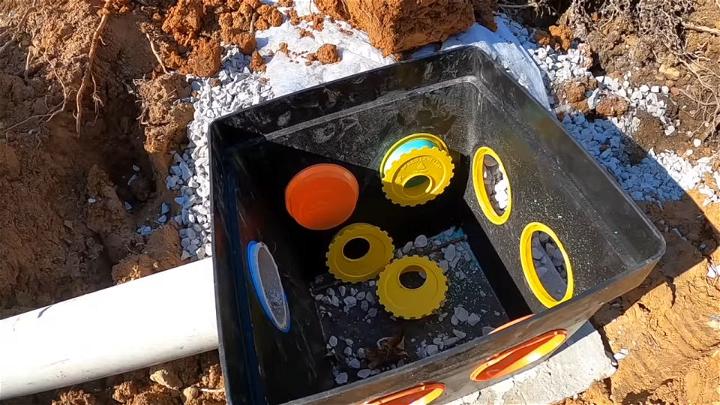

Installing an off-grid septic system brings self-sufficiency and environmental stewardship to your living space. This system is designed to function without the need for public sewage, ensuring your home remains harmonious with nature. It's an empowering choice for those aspiring to live sustainably.
6. Gallon Drum Septic Tank
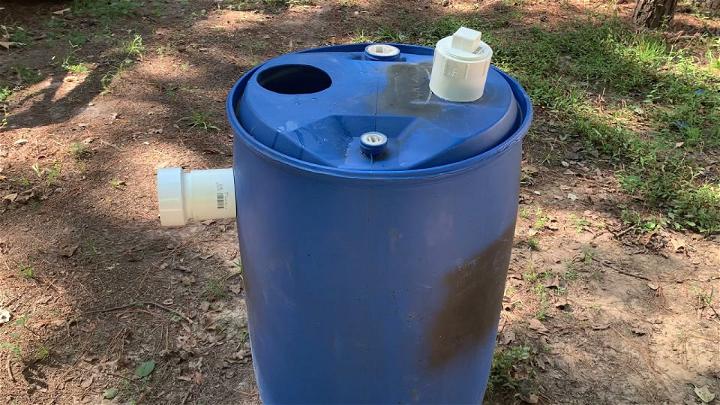

Utilizing gallon drums for your septic tank is an innovative and budget-friendly idea. This approach transforms readily available materials into a functional waste management system. It's a resourceful option for those eager to construct an effective system with minimal expenditure.
7. Off-Grid Septic System Using Totes
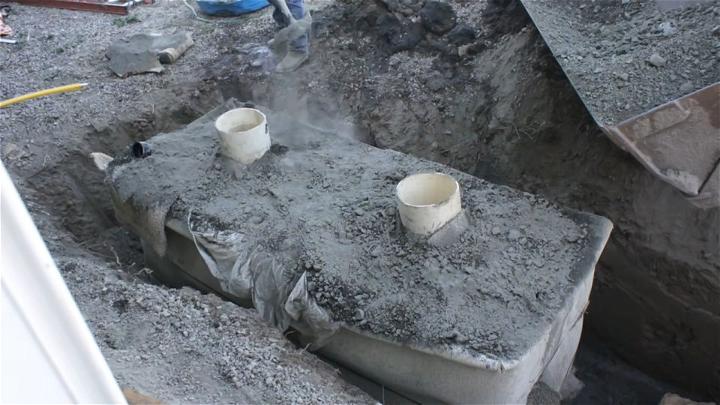

Building an off-grid septic system with totes is a testament to ingenuity and sustainability. This system capitalizes on the adaptability and availability of totes, offering a practical and eco-conscious waste solution for those living beyond the grid.
8. Simple Poly Septic Tank Installation
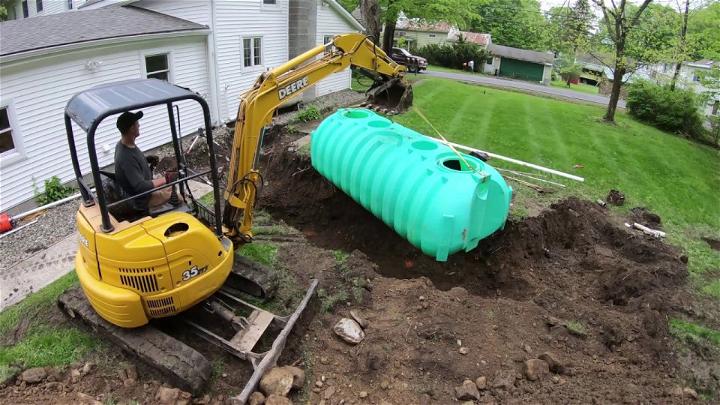

Installing a simple polyseptic tank is a straightforward and durable solution for waste management. Its polyethylene construction offers resilience against corrosion and leaks, making it a reliable choice for those seeking a fuss-free and long-lasting system.
9. Easy DIY Tiny Home Septic System

Building a septic system for a tiny home is a great DIY project. Its small design works well in tight spaces, providing a cost-effective waste solution. It's eco-friendly and easy to set up with plenty of guides available.
10. Build Your Own Septic System With Bricks and Cement
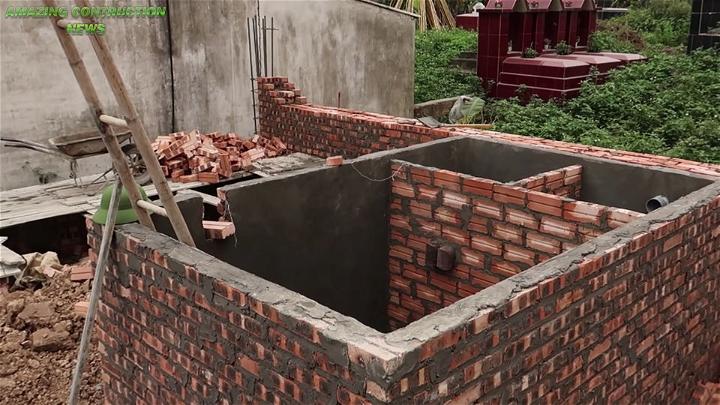

Constructing your septic system with bricks and cement is a hands-on project that promises durability and personalization. This method allows for a custom fit to your property's specific requirements, showcasing craftsmanship while ensuring a robust and effective waste management solution.
11. Handmade Septic System for Off Grid Shed to House

Living off-grid requires inventive solutions, like a handmade septic system. Crafted from natural and recycled materials, this eco-friendly choice supports your shed or house's waste management sustainably. It's a testament to self-sufficiency, minimizing environmental impact while providing a personal touch to your dwelling.
12. How to Make Your Own Gray Water Septic

Crafting a gray water septic system by yourself is a proactive step towards sustainable living. By recycling sink and shower water for irrigation, you significantly reduce water wastage. This system is an efficient, cost-effective method to manage household water, truly embodying the essence of green living.
13. DIY Septic System Installation
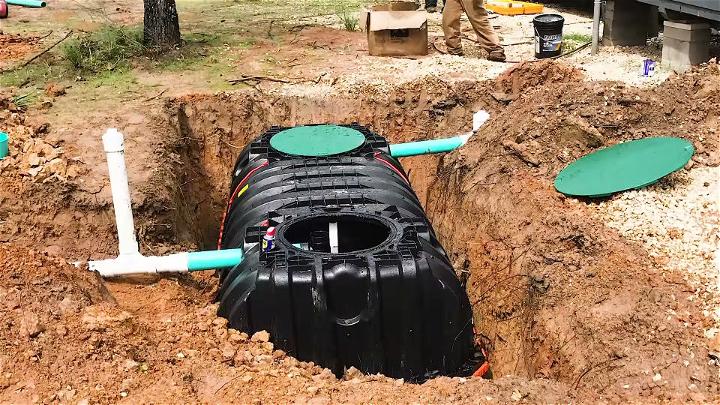

Installing a DIY septic system is a rewarding challenge that can save money and enhance your property's self-sufficiency. With careful planning and execution, homeowners can make a system that efficiently manages household waste, following local regulations and environmental practices.
14. Build Your Own Septic System
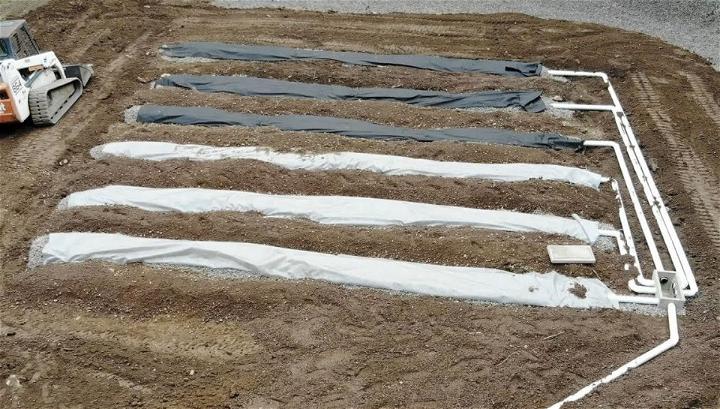

Building your septic system is a hands-on project for the dedicated homeowner. It's an opportunity to understand and implement a critical part of your home's infrastructure, resulting in pride and peace of mind knowing you've taken part in securing your home's sanitation needs.
15. Installing an Engineered Septic System
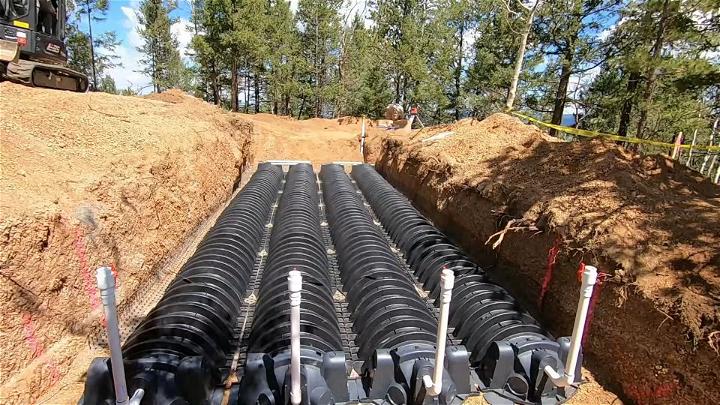

An engineered septic system offers tailored solutions for challenging properties, such as those with high groundwater or poor soil. Professional design and installation ensure optimal functionality, meeting stringent environmental standards while providing reliable waste treatment.
16. How to Build a Great Septic Tank for Toilet
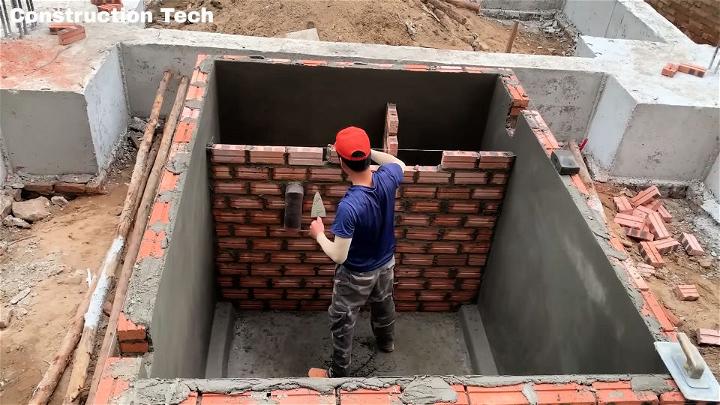

Making an efficient septic tank for your toilet is not just about functionality; it's about environmental care. A well-designed septic system manages waste safely, minimizes pollution, and recycles water naturally. Opt for durable materials, ensure proper size for household needs, and regular maintenance for a healthier, cleaner backyard.
17. Small Septic System for One Toilet
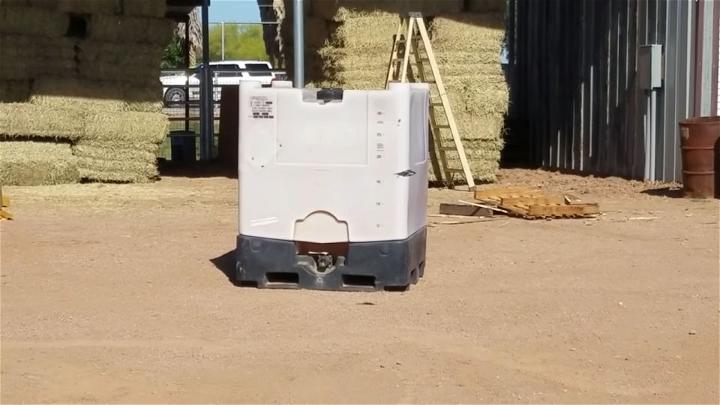

A small septic system designed for a single toilet is an ideal solution for tiny homes, workshops, or guest houses. This compact system efficiently handles limited waste, making it a practical and sustainable option for small-scale setups.
18. Do It Yourself Sewer Septic System
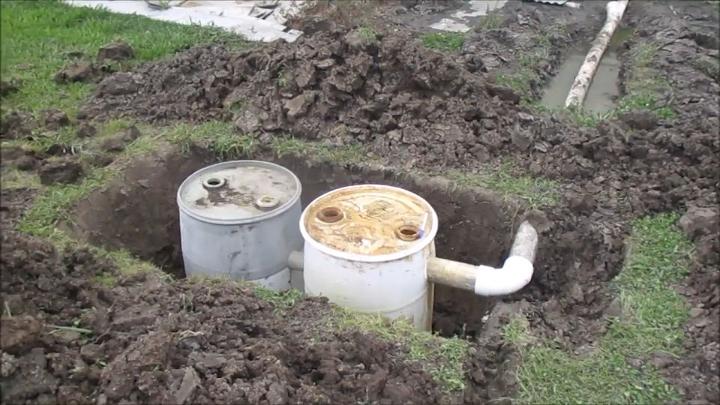

Embarking on a DIY sewer septic system project is a proactive approach to waste management. This hands-on task allows you to customize your system to meet your property's specific needs, offering a gratifying sense of achievement once completed.
19. Small Septic Tank for Cabin
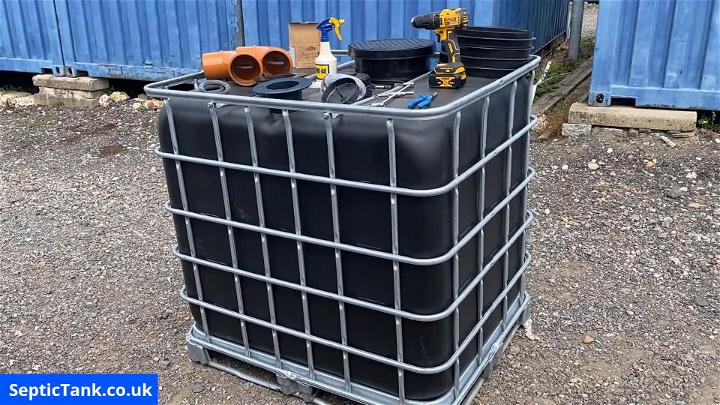

A small septic tank is perfect for a cabin, providing a simple and effective waste solution that respects the natural surroundings. It's designed to meet the needs of occasional use, ensuring your retreat remains a hassle-free haven.
20. Make Your Own Septic Tank
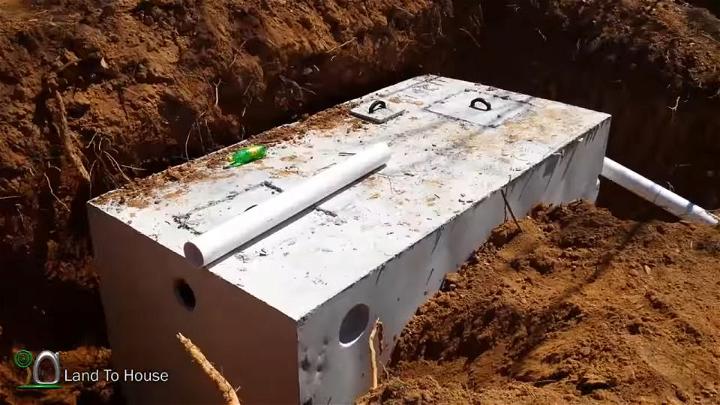

Building your septic tank is a project for those who prefer a personalized touch to waste management. This endeavor not only allows for a custom fit to your property but also provides invaluable knowledge and appreciation for the mechanics behind the scenes.
Conclusion:
Wrapping up this article, DIY septic tank installation can be a cost-effective and rewarding project for homeowners. By following the steps outlined here, you can ensure a smooth installation process and long-term functionality of your septic system. Remember to consult local regulations and seek professional assistance if needed. With proper care and maintenance, your DIY septic tank can efficiently manage household wastewater for years to come.